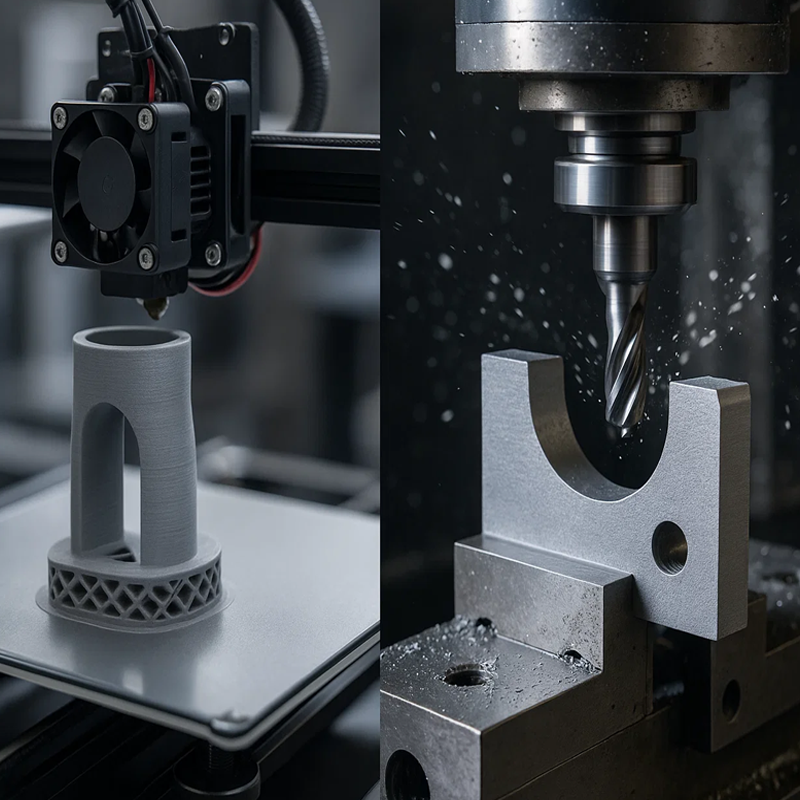
When designing a part, selecting the right manufacturing method is crucial. Making the wrong decision between CNC machining and 3D printing can lead to wasted time, money, and effort. As a designer, understanding the design requirements and limitations of each method is key to ensuring your part is manufactured efficiently and effectively. At Plantmetal, we specialize in CNC machining, but we recognize the importance of 3D printing as well, and understanding both options is essential for making informed decisions. Let’s dive into the key differences between these two powerful manufacturing techniques, so you can determine which method best suits your project needs.
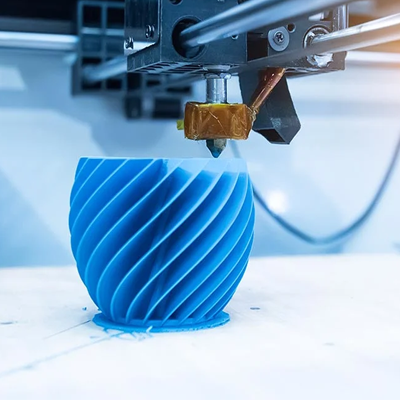

What Are CNC Machining and 3D Printing?
CNC Machining is a subtractive manufacturing process where material is removed from a solid block using cutting tools. This method requires access to the part with tools to cut away material, which can result in a smooth, precise, and strong finished product. CNC machining works on a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood, and is widely used for producing high-precision parts with tight tolerances.
On the other hand, 3D Printing is an additive manufacturing process where material is deposited layer by layer to build up a part from the ground up. This technique is particularly effective for creating complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. 3D printing is most commonly used with plastics and resins, although it can also use metals in some advanced applications.
Design Considerations: CNC Machining vs. 3D Printing
The primary distinction between these two processes lies in how they handle material: CNC machining removes material (subtractive) while 3D printing adds material (additive). These core differences directly affect how you should design your part.
CNC Machining (Subtractive Process)
Material Removal: CNC machining works by cutting away material from a solid block, which makes it a subtractive process. This requires access to the part with tools, meaning certain geometries, especially those with deep internal features or narrow openings, can be difficult or impossible to machine.
Material Options: CNC machining supports a wide range of materials, including metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium, as well as plastics, wood, and more. The material is typically a solid block that is machined down to the final part.
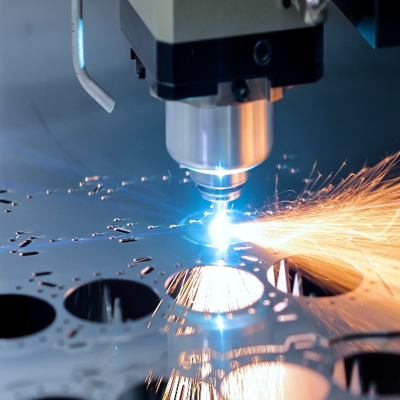

Strength: CNC-machined parts are generally stronger because they are made from a solid piece of material, with no weak points between layers.
Waste: CNC machining produces waste in the form of chips and scrap material, which can be minimized with efficient planning and cutting strategies.
Precision: CNC machining offers high precision and tight tolerances, often reaching accuracies of +/- 0.005 inches or better. This makes it ideal for applications where precise dimensions are critical.
3D Printing (Additive Process)
Material Addition: In 3D printing, material is added layer by layer, allowing for the creation of complex internal structures that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using CNC machining.
Material Options: While 3D printing is typically used with plastics and resins, advanced 3D printing technologies are also beginning to offer metal printing capabilities. However, the range of materials available for 3D printing is still somewhat limited compared to CNC machining.
Strength: The strength of 3D printed parts can vary depending on the material used and the orientation of the layers. Parts printed layer by layer can experience weak points between the layers, which can impact their strength, particularly for load-bearing applications.
Waste: One of the main benefits of 3D printing is its efficiency in material usage. Since only the necessary material is used, there is minimal waste. However, support structures may be needed for certain designs and will require post-processing to remove.
Precision: While some high-end 3D printers offer impressive resolution, the precision of 3D printed parts generally doesn’t match the tight tolerances achievable with CNC machining.
Which Method Is Better for Prototyping?
Prototyping is often a critical step in product development, and the choice of manufacturing method can significantly impact speed, cost, and functionality.
3D Printing for Prototyping: If you need a prototype quickly for form and fit testing, 3D printing is often the go-to method. It is faster and typically more affordable for low-volume production runs or one-off parts, especially when dealing with complex geometries. 3D printing allows you to create prototypes with intricate designs without the need for expensive tooling or machine setup, making it ideal for early-stage design validation.
CNC Machining for Prototyping: If your prototype needs to mimic the final production material or perform functional tests, CNC machining may be a better choice. CNC machining allows you to work with a variety of materials that closely match your final product, and the parts produced are generally stronger and more durable than 3D printed parts. Additionally, CNC machining can achieve tighter tolerances, which is important for functional prototypes that must fit with other parts or meet strict specifications.
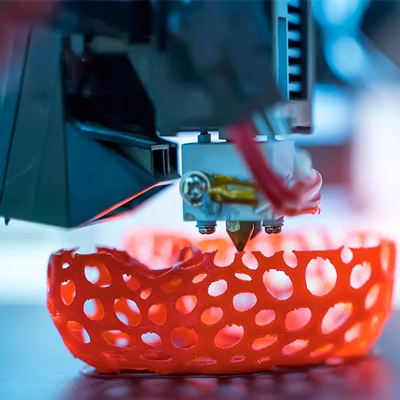

Material Considerations
Another critical difference between 3D printing and CNC machining is the range of materials available. CNC machining is incredibly versatile and can be used with a broad array of materials, including metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium, as well as plastics, composites, and even wood. This versatility makes it ideal for producing strong, durable parts for a wide range of applications.
In contrast, 3D printing materials tend to be more limited, primarily consisting of plastics, resins, and a few metals (typically in powder form). While 3D printing can be used for creating detailed prototypes or non-structural components, it may not be the best choice when strength and material properties are paramount.
Surface Finish and Post-Processing
One area where CNC machining excels is in the quality of the surface finish. CNC-machined parts typically have a smooth, clean finish, often requiring little to no post-processing, depending on the material and design. In contrast, 3D printed parts often show visible layer lines, especially if the printing resolution is low. These parts may require additional post-processing steps, such as sanding, polishing, or coating, to improve their appearance or functionality.
Conventional Machining vs. CNC Machining vs. 3D Printing
To further clarify the differences, let’s break down conventional machining, CNC machining, and 3D printing:
Conventional Machining: In conventional (manual) machining, a skilled machinist operates the machine tools, such as lathes or mills, using handwheels and levers. It’s a subtractive process, similar to CNC machining but requires more skill and is less precise.
CNC Machining: CNC machining is a fully automated subtractive process. The machine tools are controlled by a computer program, ensuring repeatability and high precision. CNC machining is ideal for high-volume production runs where precision and consistency are critical.
3D Printing: 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that builds up a part layer by layer from a digital file. It’s ideal for producing complex shapes and prototypes, but it may not always be suitable for production-grade, load-bearing parts.

Conclusion:
Choosing between CNC machining and 3D printing comes down to the specifics of your project. If you need strength, precision, and a broad range of material options, CNC machining is often the best choice. However, if your project involves complex geometries or you need a quick, cost-effective prototype, 3D printing might be the better route.
At Plantmetal, we specialize in CNC machining, offering precision machining services with a wide variety of materials to meet the needs of our clients. However, we also understand the unique advantages of 3D printing and work with clients to explore the best manufacturing options for their projects. Whether you’re looking to prototype a new part or manufacture production-grade components, we’re here to help you make the right decision for your needs.
Feel free to reach out to us at Plantmetal to discuss how we can support your next project with our expertise in CNC machining or explore the possibilities of 3D printing for your prototypes. Let’s create something great together!