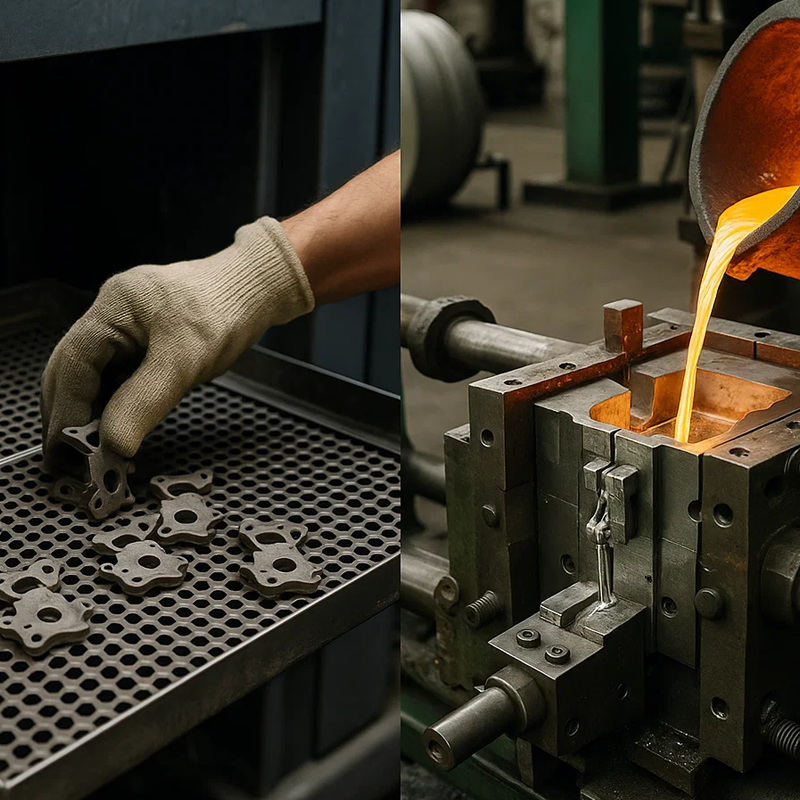
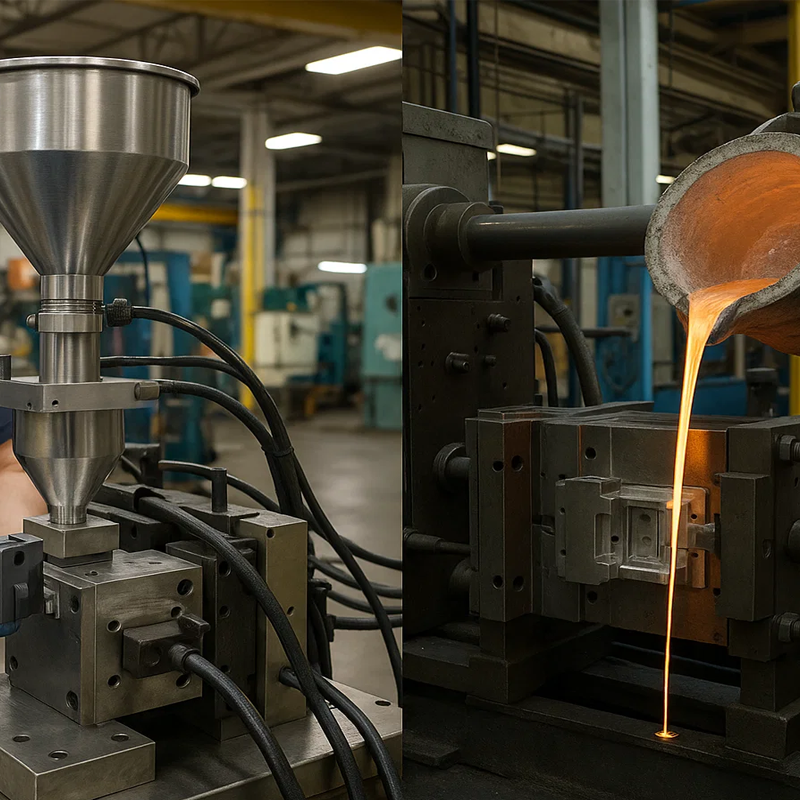
When it comes to producing precision metal components, manufacturers and product designers often face a key decision: should they choose Metal Injection Molding (MIM) or Die Casting? Both processes rely on molds to create complex shapes, but the way they process metals, achieve tolerances, and deliver cost efficiency are vastly different. Choosing the right method can significantly affect your project’s performance, lead time, and overall budget.
At Plantmetal, we understand how important this choice is for our customers. As a professional factory with years of experience in high-precision metal manufacturing, we offer one-stop service solutions that cover both MIM and die casting, along with CNC machining, stamping, and custom finishing. Our goal is to help clients—from OEMs to global suppliers—make informed decisions that balance performance and cost. In this article, we’ll break down the differences between MIM and die casting, highlighting their strengths, limitations, and best-fit applications.

What Is Metal Injection Molding (MIM)?
Metal Injection Molding combines the principles of plastic injection molding with powdered metallurgy. Fine metal powders are blended with a binder to create a feedstock, which is injected into a mold cavity. After molding, the binder is carefully removed, and the component is sintered at high temperatures.
The sintering process fuses the metal particles together, resulting in a dense, strong part that closely mirrors wrought materials. This makes MIM an excellent choice for small, intricate parts that require excellent surface quality, tight tolerances, and high-performance alloys.
Key characteristics of MIM include:
- Ability to create extremely thin walls and complex geometries
- Wide material options (stainless steel, tool steel, titanium, nickel alloys, etc.)
- Shrinkage during sintering (~15–20%), compensated during mold design
- Best suited for small components weighing just a few grams up to ~100 grams
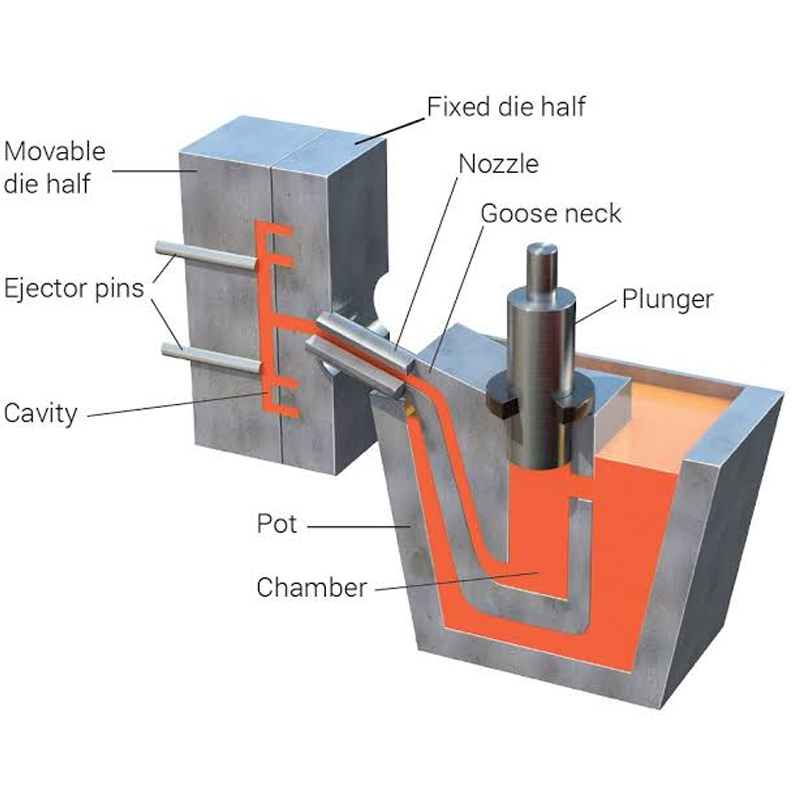
What Is Die Casting?
Die casting is a process where molten metal is injected under high pressure into a hardened steel mold. The metal solidifies inside the cavity, and the finished part is ejected, often requiring minimal post-processing.
Because die casting involves molten metals, it works best with alloys that have relatively low melting points and excellent flow properties, such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. The process is especially valuable for high-volume production of medium-to-large parts that demand repeatability and dimensional stability.
Key characteristics of die casting include:
- Fast cycle times—parts can be produced in seconds
- Excellent surface finish with minimal machining required
- Well-suited for high-volume runs with lower unit cost
- Best for larger parts or simpler geometries
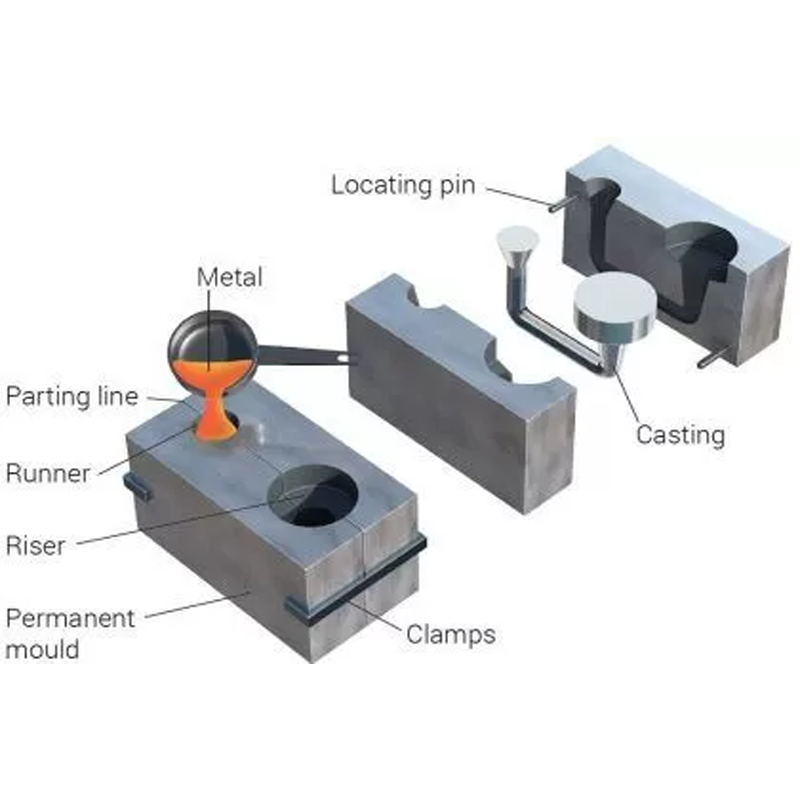
Comparing Metal Injection Molding and Die Casting
1. Process and Workflow
- MIM: Involves molding, debinding, and sintering. While more time-intensive, it enables high precision and excellent density.
- Die Casting: Injects molten metal directly into molds under pressure. Faster, but limited to low-melting alloys.
2. Material Selection
- MIM: Stainless steels, titanium alloys, tool steels, and nickel-based alloys. Ideal for industries like medical, aerospace, and defense.
- Die Casting: Aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and copper-based alloys. Common in automotive, electronics, and industrial equipment.

3. Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Finish
- MIM: Very tight tolerances (±0.3%), suitable for fine features and miniaturized parts.
- Die Casting: Good tolerances (±0.5%) with excellent surface finish, but less capable of ultra-fine details.
4. Speed and Volume
- MIM: Longer cycles due to sintering but efficient for small-to-medium batches of complex parts.
- Die Casting: Extremely fast cycles, ideal for mass production and millions of parts.
5. Cost Considerations
- MIM: Higher upfront material and processing costs due to powder metallurgy and sintering. Economical for small, complex parts requiring high performance.
- Die Casting: Higher tooling investment but lower per-unit cost at high volumes. Excellent for scaling.

Advantages and Disadvantages
Metal Injection Molding (MIM):
- Advantages: Exceptional precision, wide material choices, ideal for intricate features.
- Disadvantages: Longer lead times, higher cost for large parts, shrinkage during sintering.
Die Casting:
- Advantages: Fast production, great surface quality, cost-effective for large runs.
- Disadvantages: Limited alloys, higher risk of porosity, less suited for ultra-complex geometries.
Applications of MIM and Die Casting
- MIM Applications: Medical devices, surgical tools, aerospace components, electronic connectors, automotive precision parts, firearms, and industrial hardware.
- Die Casting Applications: Automotive housings, engine parts, appliance components, telecom hardware, consumer electronics casings, aerospace fittings, and large structural parts.

Similarities Between the Two Processes
Despite their differences, MIM and die casting share several common strengths:
- Both are mold-based processes that achieve repeatable accuracy.
- Both enable near-net shape manufacturing, reducing secondary machining.
- Both are compatible with automation, making them suitable for large-scale industrial production.
- Both provide excellent opportunities for cost optimization when designed correctly.
Which Process Should You Choose?
- Choose MIM if your project requires high-precision, small, and complex parts with fine details and advanced alloys. Industries that value strength, precision, and miniaturization often rely on MIM.
- Choose Die Casting if your project involves larger parts, high-volume production, and materials like aluminum or zinc. It’s ideal when speed and scalability are top priorities.
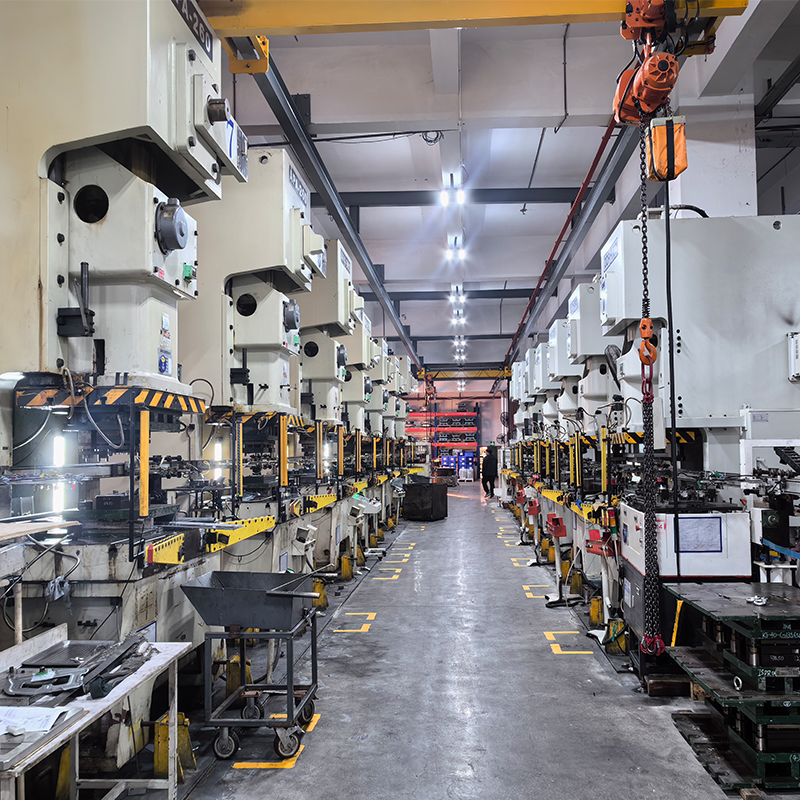
At Plantmetal, we don’t just provide one option—we provide both. As a factory with extensive expertise, we support clients with custom service and OEM service to deliver the best-fit solution for each project. Whether you’re designing a medical component, an automotive housing, or an aerospace fitting, our engineering team can guide you toward the right process.

Why Partner with Plantmetal?
- One-Stop Service – From mold design, tooling, and prototyping to mass production, machining, finishing, and assembly, everything is completed under one roof.
- High-Quality Manufacturing – With advanced equipment and rigorous quality management (ISO-certified), we ensure every part meets international standards.
- Custom Service and OEM Expertise – Our team collaborates closely with clients to tailor solutions to unique requirements, from small prototype runs to high-volume supply chains.
- Trusted Factory Experience – Years of hands-on production have made us a reliable partner for global suppliers and OEMs in automotive, aerospace, medical, and industrial markets.

Conclusion
Both Metal Injection Molding and Die Casting are powerful manufacturing technologies—but their strengths apply to different needs. MIM shines in precision and complexity, while die casting excels in speed and scale.
At Plantmetal, our mission is to give you the best of both worlds. As a professional factory and manufacturer, we deliver one-stop service solutions that combine advanced technology, reliable quality, and customized support. Whether you need intricate MIM parts or large-scale die casting runs, we’ll help you achieve efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness.

Looking for a trusted partner for your next project? Contact Plantmetal today. Our team of engineers and production experts is ready to provide the custom service and manufacturing excellence you need to bring your designs to life.