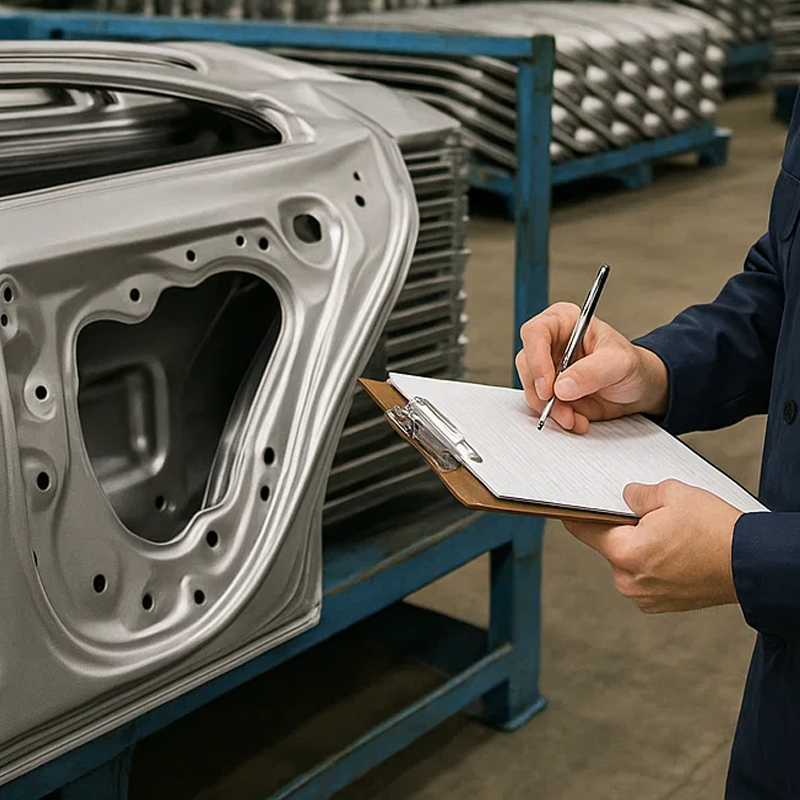
In the world of manufacturing, precision is the hallmark of quality. However, the automotive industry takes this concept to an entirely different level. If you’re sourcing stamped components for the automotive sector, you’ll quickly realize that the stakes are much higher compared to other industries. The consequences of even a small defect can be catastrophic — think safety recalls, production delays, and, in extreme cases, catastrophic failures on the road.
For manufacturers and suppliers, meeting these strict standards is non-negotiable. Automotive stamping demands exacting tolerances (sometimes as tight as 0.05mm), high-quality certifications, and stringent process controls. At Plantmetal, we understand these demands and have built our operations to ensure compliance with the highest industry standards. We provide OEM services with a focus on precision and reliability, serving clients across various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
In this blog, we’ll delve deeper into the differences between automotive stamping and other industries, and explore why partnering with a supplier who understands these standards is critical for success.

What Sets Automotive Stamping Apart?
When sourcing stamped parts for the automotive industry, the complexity of requirements is far greater than in other sectors. While a failed part in a consumer product might be inconvenient, a failure in an automotive part could lead to severe safety risks, damage, and costly recalls. Automotive parts must meet IATF 16949 standards, which is the global quality management standard specifically designed for the automotive industry. This standard ensures that automotive parts are made with zero tolerance for defects and that every process is monitored and documented to ensure safety and reliability.
At Plantmetal, we pride ourselves on being certified manufacturers, holding IATF 16949 certification to ensure the highest standards of quality. Our commitment to quality control is reflected in every stamped component we produce, from small clips to complex chassis parts.
Automotive Stamping: A High-Stakes Manufacturing Process
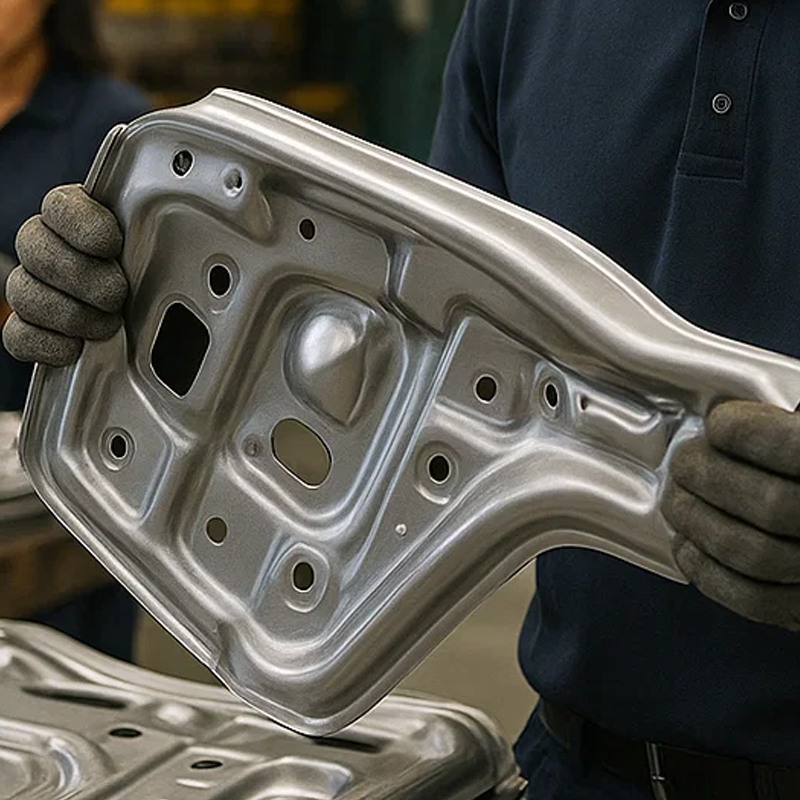
Automotive stamping involves using a die and a press to transform flat metal sheets into precisely shaped components that are integral to a vehicle’s operation. This could be everything from the body panels to the small brackets that hold essential components in place. The process requires an immense amount of precision, with some tolerances as tight as 0.05mm, ensuring each part fits perfectly within the vehicle.
Die stamping comes in various forms, with progressive stamping being one of the most widely used. In this multi-stage process, the metal strip is fed through a series of dies that gradually form the part through sequential operations. The key here is that each stage of stamping builds upon the last, allowing for high-volume production of parts that maintain consistent quality and accuracy. However, the complexity doesn’t stop there. We also use Fourslide stamping for more intricate parts, providing multi-directional motion to achieve complex bends and shapes.
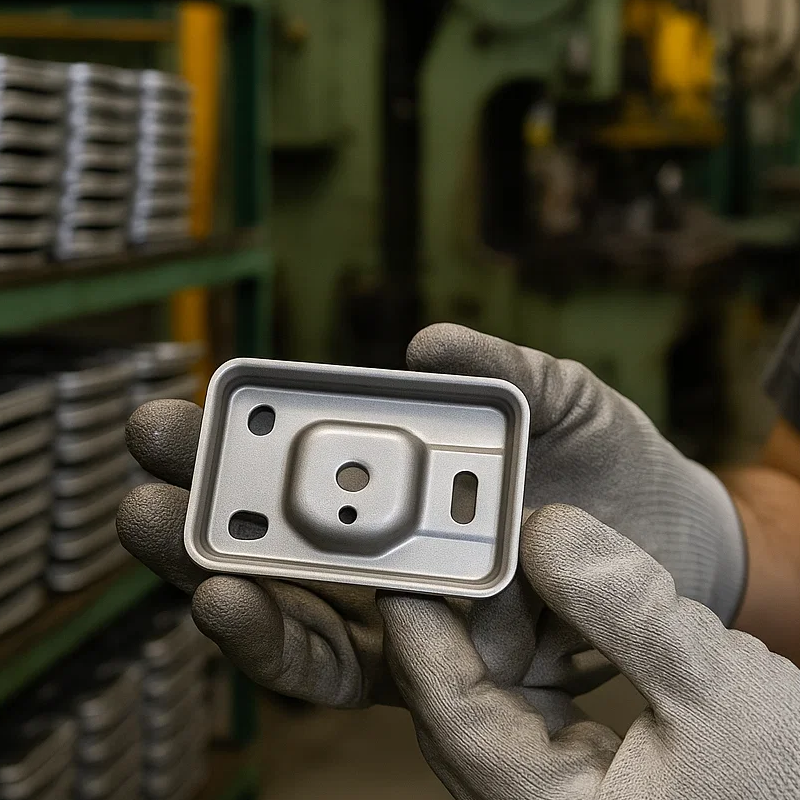

The Need for Certification in Automotive Stamping
One of the most significant differences between automotive stamping and other industries is the level of process control required. Certification like IATF 16949 is more than a mere formality; it is the backbone of automotive manufacturing. This certification ensures that manufacturers have a robust quality management system (QMS) in place, covering everything from Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) to Production Part Approval Process (PPAP). This means we are held accountable for each step of the process and must proactively manage and mitigate risks.
At Plantmetal, we take these standards seriously. Our certification allows us to not only guarantee the quality of each part but also ensure that every component is traceable, from raw material to final product. Through tools like Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), we identify potential risks in the manufacturing process and take proactive steps to address them, ensuring that our automotive parts consistently meet the stringent standards expected by our clients.
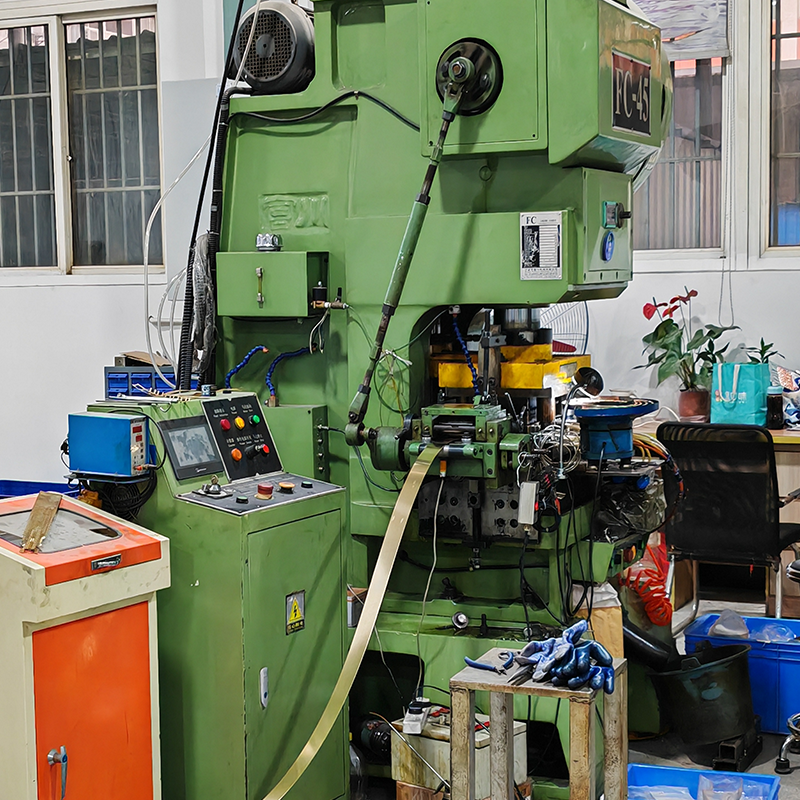

How Stamped Parts are Used Across Various Industries
While automotive stamping has the highest stakes, stamped parts are not exclusive to the automotive industry. In fact, they’re used in a variety of industries, and the level of precision required varies based on the final application.
Here’s a breakdown of how stamped parts are used in different sectors:
| Industry | Common Applications | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Brackets, clips, sensors, engine mounts, seat frames | Safety, reliability, IATF 16949 |
| Electronics | EMI shields, connectors, contacts, lead frames, heat sinks | Miniaturization, electrical conductivity |
| Medical | Surgical instruments, diagnostic housing, implantable devices | Biocompatibility, extreme precision |
| Industrial | Levers, mounting plates, retainers, fasteners | Durability, strength, cost-efficiency |
| Aerospace | Brackets, clamps, fuselage components | High strength, extreme heat resistance |
In each of these sectors, the requirements vary significantly. For example, while the automotive industry places an emphasis on safety, the aerospace sector requires parts that can withstand extreme conditions. At Plantmetal, we provide a one-stop service for all these industries, ensuring that each part we manufacture meets the specific quality standards of its intended use. Our team works closely with clients to tailor every aspect of the production process, from design consultation to final part approval.
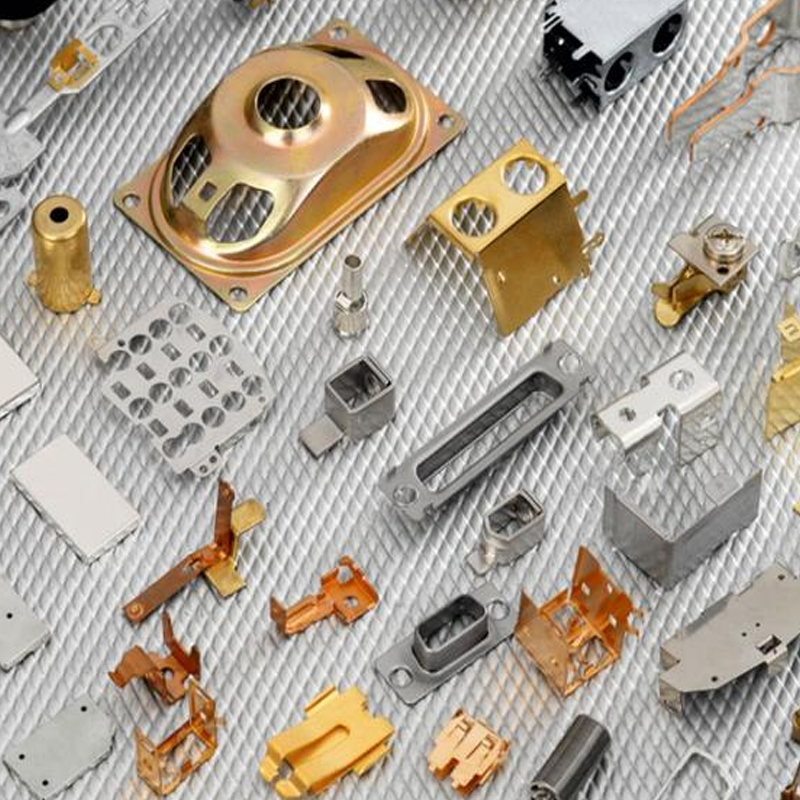

Metal Stamping: The Essential Manufacturing Process
So, what exactly is metal stamping, and how does it work? Metal stamping is a cold-forming process that uses a press and die to transform flat metal sheets into the final part. The metal is cut, bent, or formed into precise shapes, making it an ideal solution for high-volume production.
At Plantmetal, we specialize in two key types of metal stamping: progressive die stamping and Fourslide stamping. Progressive die stamping is used for more complex parts that require multiple stages to achieve the final shape. Fourslide stamping, on the other hand, is ideal for parts with intricate bends or multiple angles, like clips or springs. Both processes allow us to produce parts at high speed while maintaining tight tolerances.

Conclusion:
When it comes to automotive stamping, the standards are strict, and the stakes are high. A single defect could result in costly recalls or safety issues. That’s why it’s critical to partner with a supplier who not only understands the unique demands of automotive manufacturing but also has the capabilities to meet them.
At Plantmetal, we have over a decade of experience in producing high-precision stamped parts for a variety of industries, with a strong focus on automotive. Our OEM services are tailored to ensure that every component we manufacture meets the highest standards, and our one-stop service makes it easy for our clients to streamline their production processes. We offer custom services for everything from initial design consultations to final production — ensuring that your project is in expert hands every step of the way.

Contact us today to learn more about how we can help with your stamping needs. Whether you need a high-volume batch of automotive parts or specialized components for a different industry, Plantmetal is here to deliver quality, precision, and efficiency. Let’s work together to turn your ideas into reality with precision-crafted parts you can trust!